Are you seeking a responsible way to dispose of your old tech? Finding a trustworthy e-waste collector is the first step to ensuring your electronics are recycled properly. Our guide offers a deep dive into collection methods, the recycling journey, compliance, and how individuals and businesses can participate in ecological recovery.
Key Takeaways
- E-waste collection services offer various convenient options, such as bins, take-back programs, and online pickup scheduling. These options are crucial for preventing environmental harm and conserving resources through proper disposal and recycling.
- The e-waste recycling process involves pre-processing to remove hazardous components, mechanical processing to separate materials, and the extraction of valuable metals. This contributes to pollution reduction, carbon emissions mitigation, and the promotion of a circular economy.
- Compliance with disposal regulations like the Universal Waste Rule and the EWRA is essential to avoid the negative impact of hazardous materials, and technological advancements in the industry are improving the efficiency of material recovery and recycling.
Navigating E-Waste Collection Services
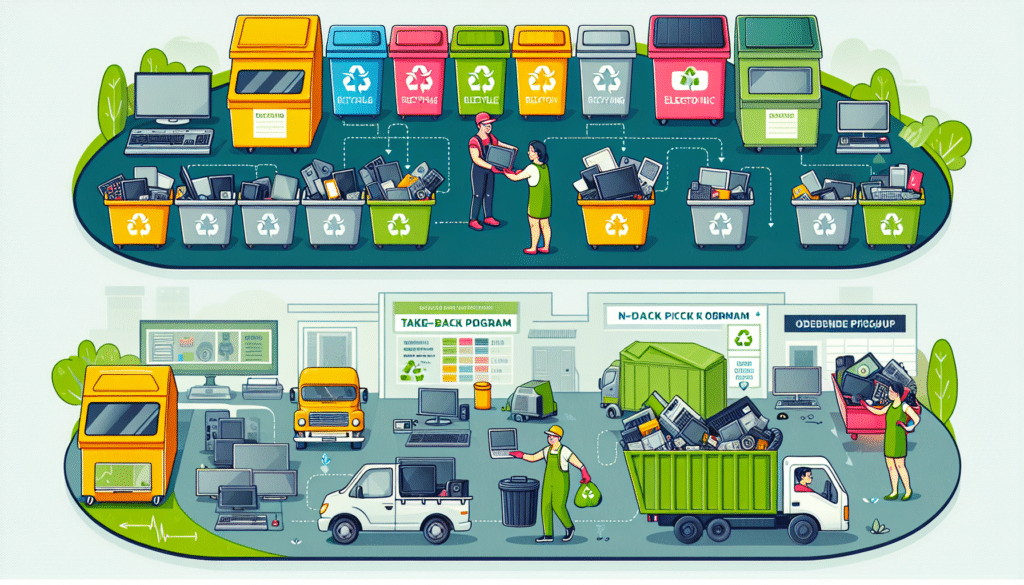
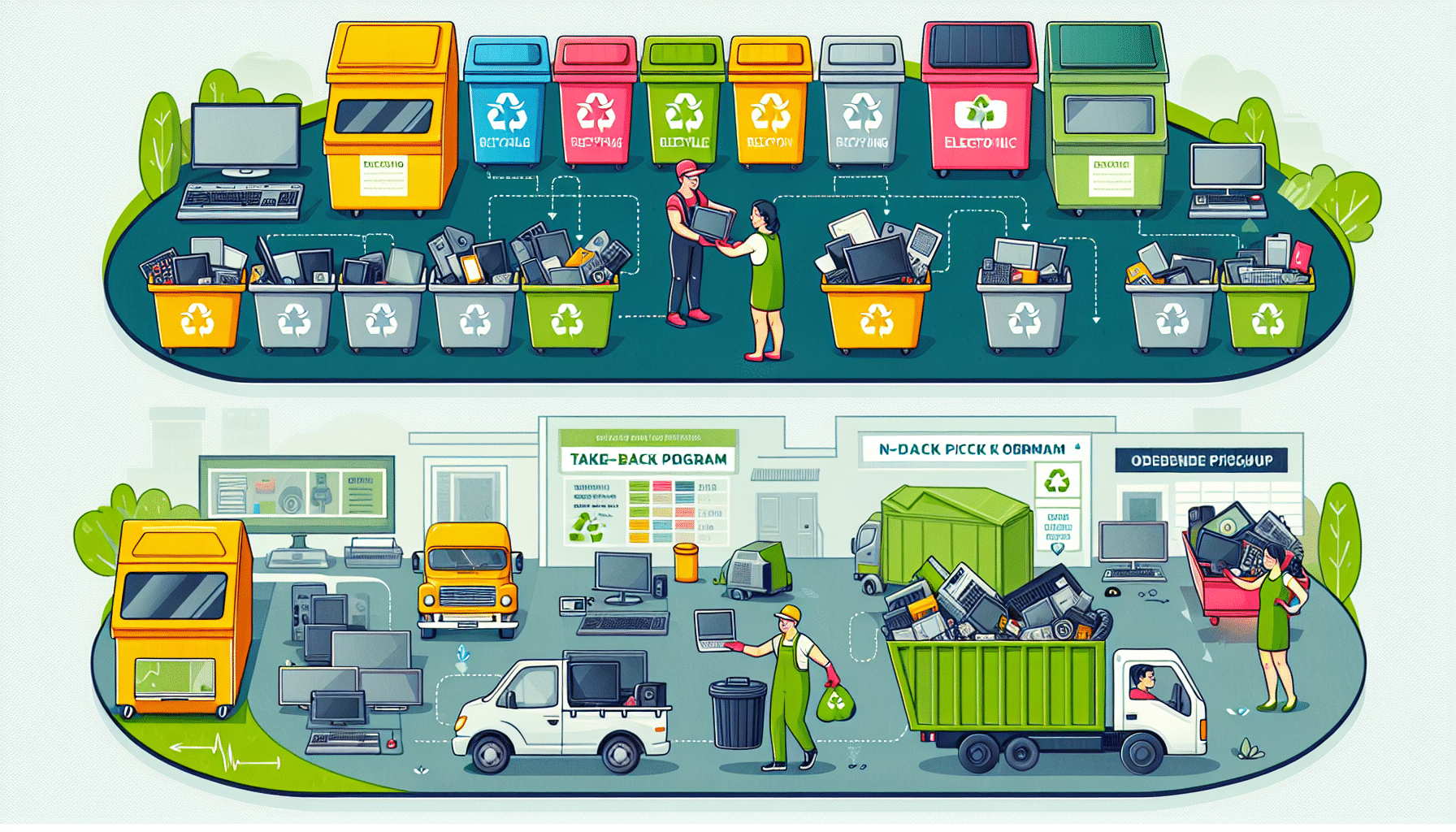
Have you ever wondered about the fate of your outdated electronic items? Responsible e-waste disposal starts with easy-to-use collection services, helping you to discard obsolete electronics, including covered electronic devices. From recycling bins to take-back programs and on-demand pickups, many options exist to ensure your electronic waste doesn’t end up in a landfill, where hazardous substances could harm the environment. For the ultimate convenience, some e-waste collection sites offer user-friendly online systems that allow you to:
- Schedule doorstep collections
- Track the progress of your collection
- Receive notifications about upcoming collections
- Easily contribute to e-waste recycling
Furthermore, a successful e-waste management system hinges on collaboration between e-waste collectors and local recycling facilities. These partnerships are vital to ensure the proper disposal and recycling of collected electronic waste. By playing this pivotal role, e-waste collectors not only prevent potential harm to the environment but also help conserve valuable resources.
The Journey of Your Electronic Waste
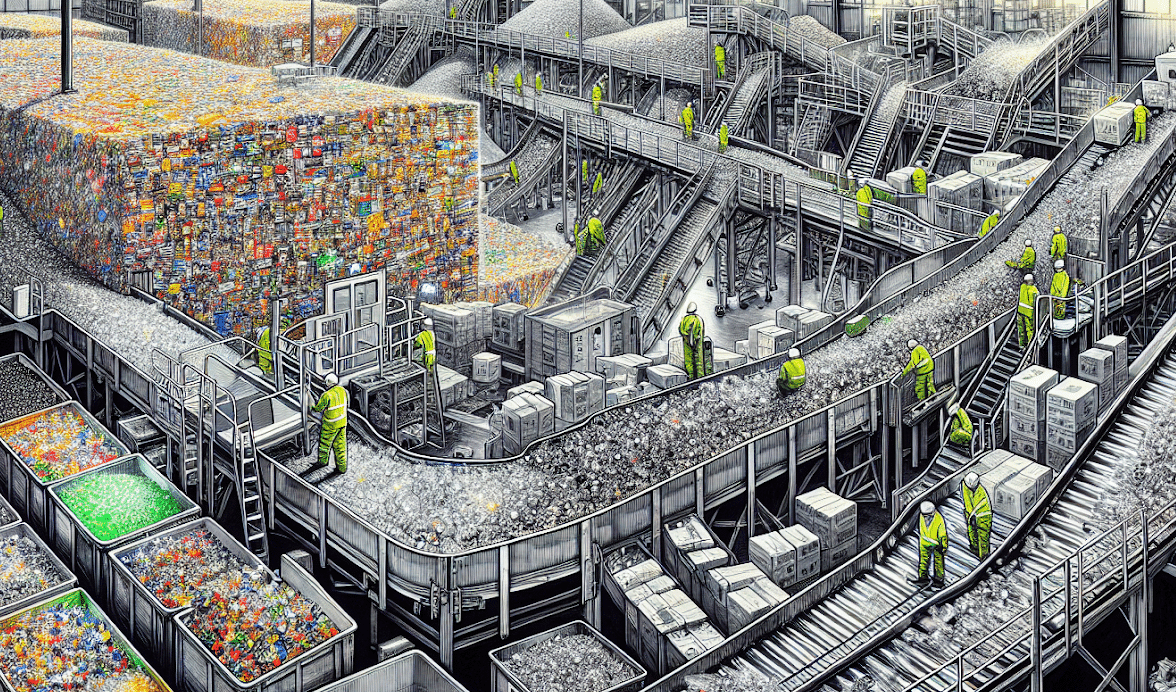
Upon collection, your electronic waste sets off on an environmentally friendly journey. The initial pre-processing phase involves weighing shipments and removing hazardous components like batteries and cathode ray tubes. This meticulous sorting ensures that each material is dealt with appropriately. Mechanical processing takes the stage following pre-processing, utilizing advanced separation technologies to break down e-waste into material fractions.
The culmination of this journey sees valuable metals like:
- Iron
- Steel
- Aluminum
- Copper
Extracted and prepared for their next life in the manufacturing of new products, recycling reduces waste. It contributes to human health by reducing pollution, carbon emissions, and the need for virgin raw materials. By choosing to recycle and reuse, you’re partaking in a circular economy that significantly benefits our environment.
Ensuring Environmental Compliance in E-Waste Disposal
Understanding and adhering to e-waste disposal regulations is paramount in our quest to safeguard the planet. In Southern California, e-waste disposal is strictly regulated under the Universal Waste Rule and the Electronic Waste Recycling Act (EWRA). Additionally, e-waste collectors must align their practices with the Responsible Battery Recycling Act, ensuring safe and compliant battery disposal.
The Department of Toxic Substances Control (DTSC) serves as a regulatory watchdog, enforcing compliance with these regulations to safeguard the environment and public health from the hazards posed by improper e-waste disposal, including hazardous waste. By adhering to these standards, e-waste collectors play a fundamental role in preventing the detrimental impact of hazardous materials on our soil and water.
Advanced Technology in E-Waste Collection and Recycling
Innovation is key to electronic recycling, especially for electronic devices like cell phones. Advanced technologies such as infrared cameras, air jets, and plastic separation techniques are revolutionizing the way materials are extracted from electronic waste. Alongside this, the emergence of robotic systems and eco-friendly metal extraction processes is streamlining the e-waste recycling workflow.
Artificial intelligence further enhances the precision of material identification and separation, propelling recycling facilities toward greater efficiency. The push towards a circular economy also sees advancements in biodegradable materials, eco-friendly packaging, and energy recovery methods, expanding the horizons of e-waste recycling.
Partnering with Businesses for E-Waste Management
Businesses wield a considerable influence in the realm of e-waste management. Giants like Google and Apple have realized this potential and are collaborating with recycling firms to bolster e-waste recycling efforts. These partnerships are not purely environmental gestures; they’re strategic moves to reintegrate recovered materials back into the supply chain, reducing costs and enhancing sustainability.
Local businesses, too, can benefit from partnering with e-waste recycling services. By leveraging their existing infrastructure, companies can boost their environmental reputation and contribute to the recycling movement. Furthermore, many of these e-waste management programs offer subsidized collection services to encourage consumer participation, making it easier and more affordable for individuals to recycle.
Engaging the Community in E-Waste Recycling Efforts
Community participation often determines the success of e-waste recycling initiatives. Awareness campaigns and community recycling events provide residents with the knowledge and opportunity to dispose of their e-waste responsibly. Furthermore, social media groups can serve as powerful tools to foster ongoing communication and bolster community recycling efforts.
Recognizing and tackling obstacles to recycling, like ‘product hibernation’ and the habit of hoarding unused electronics, is critical to enhancing recycling rates. Through dedicated efforts and educational outreach, communities can play a significant role in ensuring electronic waste recovery and responsible disposal.
Summary
As we’ve navigated through the intricacies of e-waste collection and recycling, one thing remains clear: our collective efforts are crucial in shaping a sustainable future. From responsible disposal and adherence to environmental regulations to embracing technological advancements and fostering partnerships, every action we take influences the fate of our planet. Let’s continue to strive for a world where electronic waste is viewed not as a burden but as a resource for innovation and sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is e-waste banned?
E-waste is banned to protect the environment and human health from the potential threats posed by improperly treated and disposed electronic devices.
What are some common e-waste items that need to be recycled properly?
Common e-waste items that need to be recycled properly include cell phones, computers, televisions, batteries, and other electronic devices containing hazardous materials. Proper recycling of these items is crucial for environmental safety.
Why is it important to use e-waste recycling services?
Using e-waste recycling services is crucial because it prevents environmental pollution and promotes the reuse of valuable materials by ensuring hazardous materials are not disposed of in landfills.
How does technology enhance e-waste recycling processes?
Technology like AI, robotics, and advanced sorting techniques increase the efficiency and accuracy of material separation, leading to more sustainable e-waste recycling practices.
Can businesses benefit from partnering with e-waste recycling companies?
Partnering with e-waste recycling companies can help businesses improve their environmental reputation, reduce waste management costs, and reintegrate recovered materials into their supply chains.